Setting up Business in India
Starting Business in India
India as a Prime Destination for Foreign Business Expansion.
For foreign investors, selecting the right business entity is crucial for long-term success. Choosing a structure that aligns with their operational and strategic goals is essential. With expert guidance from business setup consultants in India, companies can establish a strong presence, navigate the regulatory landscape, and leverage the vast opportunities India’s dynamic market offers.
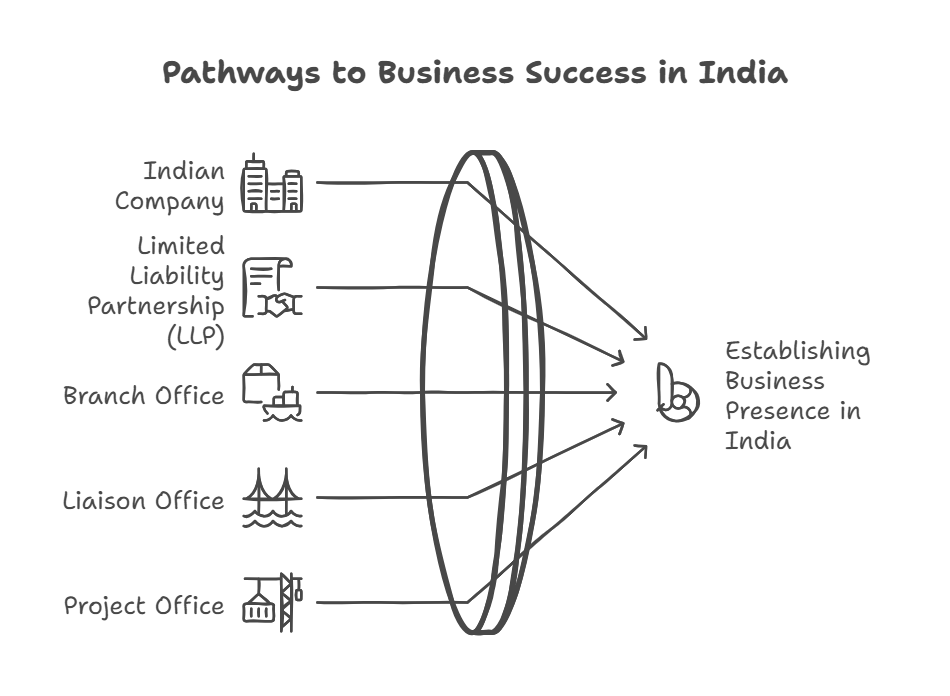
How can Foreign investors establish a business in India?
Indian Company
Entrepreneurs can set up either a Private Limited Company or Public Limited Company, allowing variations like:
- Wholly owned Subsidiary
- Joint Venture
- Ownership by Foreign Resident
Limited Liability Partnership
Combining features of a Partnership Firm and a Company, LLP permits 100% FDI investment through the Automatic Route
Foreign Company
It is the set-up for carrying out Import, Export, Research, and execution of projects. It can be registered as:
- Branch Office: Engages in Import, Export, Research, and Consultancy activities.
- Liaison Office/ Representative Office: Represents the foreign parent company in India.
- Project Office: Operates as per contract of a specific project.
Structure of Business Establishment
| Particulars | Wholly Owned Subsidiary | Joint Venture | Ownership by Foreign Individual |
|---|---|---|---|
| About | A company wholly owned, managed, and controlled by the parent company | An arrangement between multiple parties forming a separate legal entity, e.g., a Company, LLP, or partnership | A company wholly owned, managed, and controlled by the foreign individual/s |
| Ownership | Solely owned by the parent company | Shared ownership among entities forming the Joint Venture | Solely owned by the foreign individual |
| Control & Management | By Parent company | Governed collectively by all involved entities through a Joint Venture Agreement | By foreign individual |
| Taxation | India | India | India |
| Liability | Parent company not personally liable for subsidiary’s debts and obligations | Entities share responsibilities jointly or severally based on the agreement for the obligations of the Joint Venture | Foreign individual not personally liable for Indian company’s debts and obligations |
Types of Business Establishment in India
Explore Diverse Business Structures in India: A comprehensive overview of establishment types, compliance essentials, and key criteria for various business entities under Indian law.
| Particulars | One Person Company (OPC) | Private Limited | Public Limited | LLP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governing Act/ Law | Companies Act, 2013 | Companies Act, 2013 | Companies Act, 2013 | LLP Act, 2008 |
| Separate legal Identity | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Defaults Liability | Directors | Directors | Directors | Designated Partners |
| Members Min/Max | 1/1 | 2/200 | 7/No Limit | 2 Designated Partners/No Limit |
| Directors Min/Max | 1/15 | 2/15* | 3/15* | 2 Designated Partners/No Limit |
| Resident Director | 1 Mandatory (NRI permitted) | 1 Mandatory | 1 Mandatory | 1 Mandatory (NRI permitted) |
| Public Subscription of shares | Not allowed | Not allowed | Allowed | Not allowed |
| Income Tax Rate | Ranging from 17.16% to 34.94% | Ranging from 17.16% to 34.94% | Ranging from 17.16% to 34.94% | Ranging from 17.16% to 34.94% |
| Audit | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory* (limit based) |
A company can appoint more than 15 directors by passing a special resolution in a general meeting.
(Including surcharge and education cess)
Resident Director Requirement:
Every company must have at least one director who has resided in India for a minimum of 182 days during the financial year (120 days for LLPs and OPCs) and in each subsequent year.
Establishment in India: Offices for Foreign Companies – Liaison
Office | Branch Office | Project Office
Foreign companies setting up offices in India must comply with specific regulations and guidelines. Here’s a comprehensive guide covering the key requirements and processes.
Liaison Office (LO)
Serves as a communication link between the foreign company’s head office and Indian entities -Not allowed to engage in commercial activities
Branch Office (BO)
Engages in import/export, professional services, research, technical collaborations, etc.
Project Office (PO)
Liaison Office (LO)
Foreign entities with a profitable track record for the preceding three financial years and – a net worth of USD 50,000 or moreServes as a communication link between the foreign company’s head office and Indian entities -Not allowed to engage in commercial activities
Branch Office (BO)
Foreign entities with a profitable track record for the preceding five financial years and – a net worth of USD 100,000 or more
Project Office (PO)
Liaison Office (LO)
Typically, 3 years (2 years for NBFCs, construction, and development sectors)
Branch Office (BO)
Continues until the office closure
Project Office (PO)
Duration based on the project
Liaison Office (LO)
Not applicable
Branch Office (BO)
Ranging from 41.60% to 43.88 #*
Project Office (PO)
Ranging from 41.60% to 43.88 #*
Liaison Office (LO)
Not applicable
Branch Office (BO)
Allowed to remit net of taxes
Project Office (PO)
Allowed to remit net of taxes
Initiating a Business: The Registration Journey (Process) Simplified
From acquiring digital signatures to obtaining essential documentation, here’s a simplified step-by-step guide to registering both Companies and Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs). Alternatively, you can streamline the process by opting for professional business setup consultancy services in India.

- Get Digital Signature Certificates for Directors and Shareholders
- Check the proposed name with the relevant authority
- Check for registered trademark and proposed name conflict
- Submit forms for Name Approval
- Prepare charter documents
- File incorporation forms
-
Obtain Tax Registration :
a) Permanent Account Number (PAN)
b) Tax deduction / collection Account Number (TAN) - Open a Bank Account, Deposit initial capital
- File relevant form for initiating the business operations

- Get Digital Signature Certificates for Designated Partners
- Check the proposed name with the relevant authority
- File relevant form for Name Approval
- Submit forms for incorporation
- Obtain a Certificate of Incorporation
- File incorporation forms
-
Obtain Tax Registration :
a) Permanent Account Number (PAN)
b) Tax deduction / collection Account Number (TAN) - Prepare LLP Agreement
- Open Bank Account, Deposit the initial capital
- File relevant form for initiating the business operations
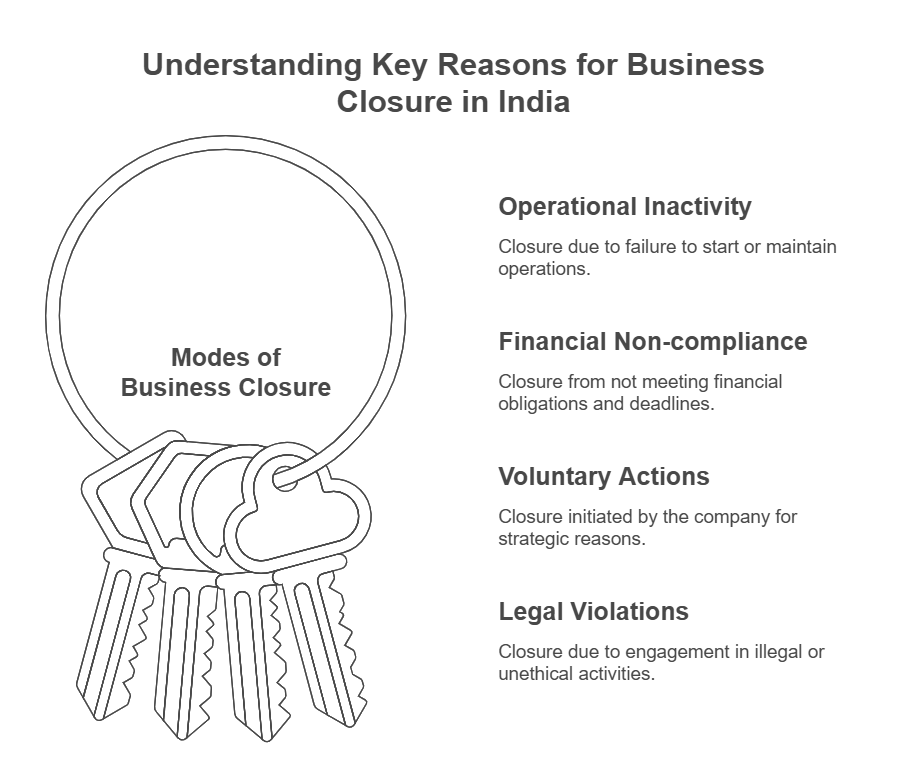
Understanding Business Closure Procedures in India
Here’s a concise breakdown of the closure process in compliance with Indian regulations:
The scenarios for business closure include:
Note: It’s always prudent to double-check the latest regulations and guidelines and reach out to the business setup consultants in India before making decisions regarding business setups or closures. For further assistance or further queries, please get in touch with us anytime. We’re here to help!
FAQs
1. How to start a business in India?
The forms of establishing a company in India are as follows:
- Public limited company
- Private limited company
- One person company (OPC)
- Section 8 company
Other forms of setting up business in India are listed here under:
- Sole proprietorship
- Partnership firm
- Limited liability partnership (LLP)
2. What are the factors to consider when choosing a business entity?
The factors which are to be considered while choosing a business entity are as follows:
- Tax Treatment
- Ability to raise capital
- Separation of ownership and management
- Limited liability protection
- Transferral of ownership
- Ease of formation
3. How to establish a foreign company in India?
Prior consent from RBI and/or government is required for setting a business venture in India by a Liaison Office/ Project Office/ Branch office. Also, the set-up to open a Branch Office / Project Office/ Branch Office/ Liaison Office is that only a body corporate consolidated outside India can include any of these offices.
4. What are the legal requirements for starting an occupation in India?
The legal necessities for starting a business in India are:
- Formalizing a business structure and founders agreement.
- Applying for business licenses.
- Understanding taxation and accounting laws.
- Adhering to labor laws.
- Ensuring protection of intellectual property.
- Providing effective contract management.
- Details about winding down the business.
5. Name the steps which are to be followed for registering a business in India.
The steps which needs to be followed for registering a business in India are:
- Checking the company name availability.
- Acquiring a direct identification number (DIN).
- Receiving a digital signature certificate.
- Obtaining an incorporation certificate.
- Creating a company seal for official documentation.
- Stamping of all company documents.
- Acquiring a permanent account number (PAN).
- Receiving a tax account number (TAN).
- Acquiring a certificate from the State/Municipal inspector under the Shops and establishing act.
- Applying for GST registration.
- Obtaining a professional tax certificate from the state professional tax office
- Completing a national employees’ provident fund registration.
6. What services do you provide for starting up a business in India?
At Guidewell INT, the following services are offered for starting a business in India:
- Business entry advisory services
- Recognizing the suitable form of business
- Acquisition of licenses and registration under various acts
- Addition of permanent account number (PAN)/ tax deduction or collection account number (TAN)
- Preparation and filing of incorporation documents
- Attestation and legalization of documents
- A fling of application with RBI through Authorized Dealer Bank
- Verification of knowing your client (KYC) from the banker of the parent company
- Registration of project office of a foreign company with the ROC
- Preparing charter documents (Memorandum of Association/ Articles of Association)
- Assistance in trademark & other intellectual property registration.
- Secretarial and administrative support.
- Post incorporation services (accounting, bookkeeping, payroll, auditing, taxation etc.)
- Assistance in RBI compliances.
